What are English tenses?
The grammatical tenses used in the English language refer to different forms of verbs and indicate at what time something happens: past, present or future. They are language time clocks.
A calendar does not say anything, but along with telling your listener the sort of action you are describing, temporal structures tell your listener at which point in time this action is occurring.
Meaning is defined by tense in English. Without it, you would have the sound of a time traveler who never unpacks. Want to write about a memory? What you require is the past tense. Giving directions? You will grab the present. Making plans? The future is your friend. Action timelines make communication simple to follow and real.
Tenses are a part of our lives, even when we are not conscious of them:
-
Presentation style
Iencountered him at the airport. As usual, he was late. -
Instructional giving
Press this button, and then itstarts . -
Discussion about experiences
Ihave visited Japan two times. -
Making promises or prophesies
Iwill call you back tomorrow.
In the English language, every tense takes us through time. Here is the way each of them works out in a sentence:
-
Past
Idrank coffee before sunrise yesterday. -
Present
Idrink coffee before sunrise every morning. -
Future
Iwill drink coffee before sunrise tomorrow.
Level up your English with Koto!
General structure of tenses in English grammar
Tenses give the context to actions, whether they are in the middle of progress, have been done, or will happen in the future.
All the tenses in the English language possess three principal constituents:
Subject is the doer of the action (e.g., I, she, they).
Verb indicates the phenomenon or condition. It varies with the tense.
Time marker (optional) gives the time of action.
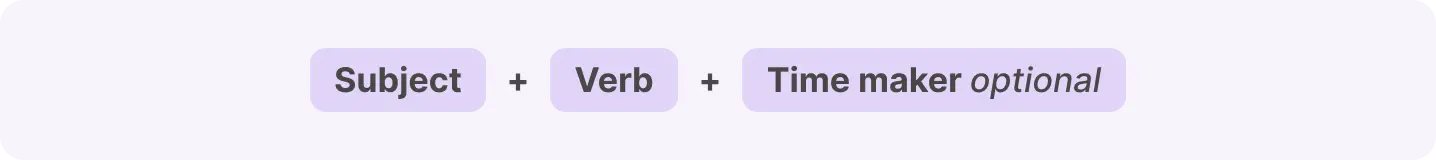

The combination of these elements creates the foundation for correct tense usage:
Grandpa (subject) tells (verb) stories to the children every night (time marker).
The formula of each type of tenses is evident. Knowing these patterns, you will be able to easily build sentences that will describe time correctly. The following table provides the description of the key structures with examples.
| Tense | Structure / Scheme | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | Subject + base verb (s/es) |
Daniel
|
| Present Continuous | Subject + am/is/are + verb-ing |
Sophie
|
| Present Perfect | Subject + has/have + past participle |
We
|
| Present Perfect Continuous | Subject + has/have + been + verb-ing |
Oliver
|
| Past Simple | Subject + past verb |
The children
|
| Past Continuous | Subject + was/were + verb-ing |
Jack
|
| Past Perfect | Subject + had + past participle |
They
|
| Past Perfect Continuous | Subject + had + been + verb-ing |
The workers
|
| Future Simple | Subject + will + base verb |
We
|
| Future Continuous | Subject + will be + verb-ing |
At 10 AM next Monday, the engineers
|
| Future Perfect | Subject + will have + past participle |
By next week, the team
|
| Future Perfect Continuous | Subject + will have been + verb-ing |
In September, Lucas
|
These tense schemes in mind make the process of formulating sentences an easy one. They provide the structure you need to link actions to time effectively.
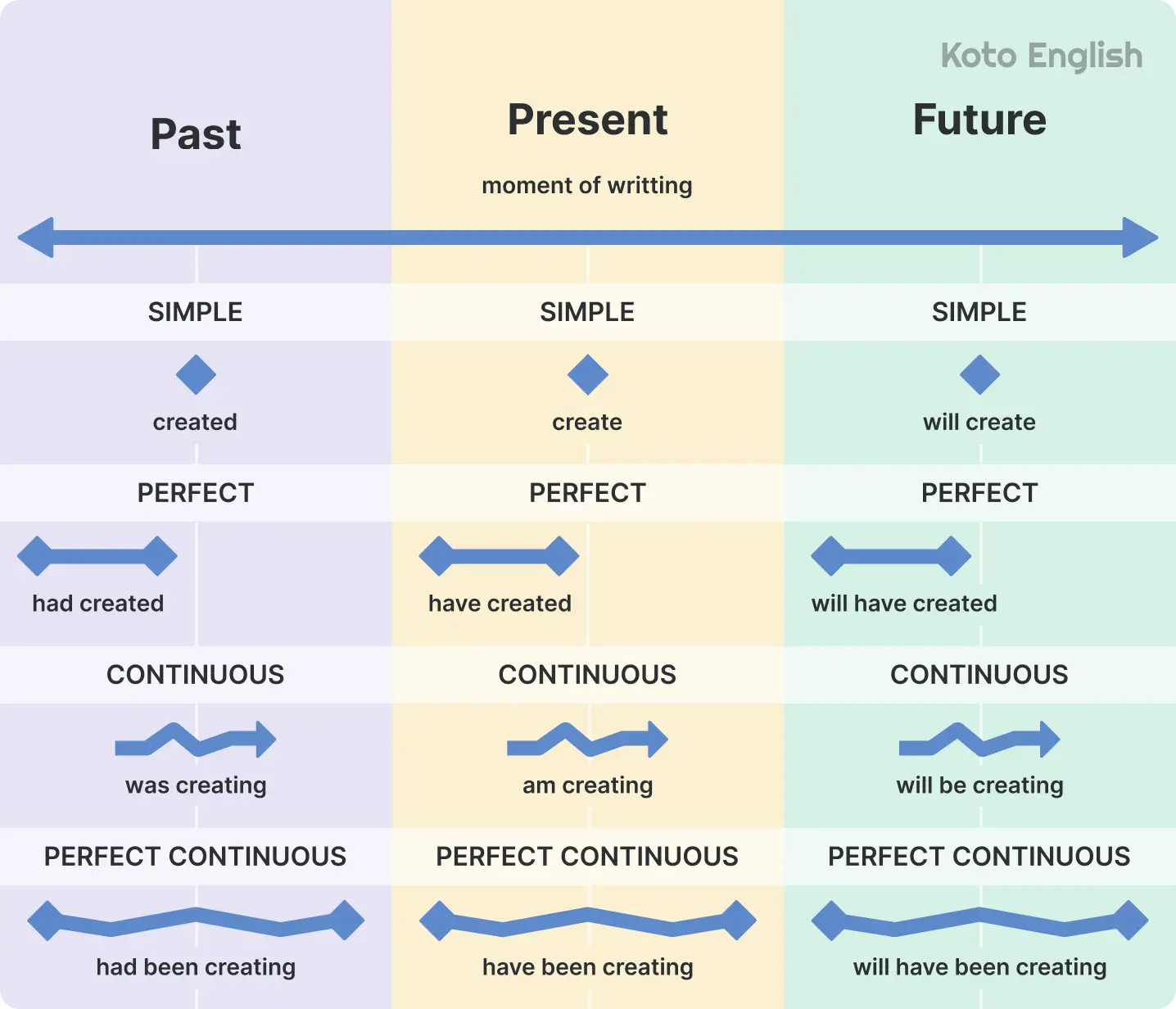
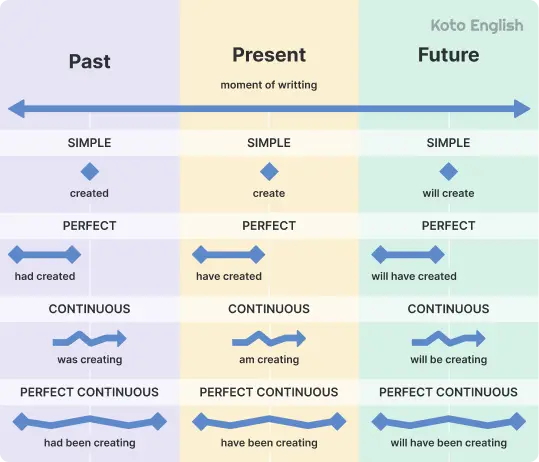
Types of grammar tenses
English tense forms are like time stamps for your sentences: past, present, or future. Grammar tenses help you explain what’s going on, what went down, or what’s coming next. Once you get the hang of them, your stories sound smoother and your questions make more sense.


Present tenses
Wondering how all tenses actually work in real conversations? We will assist you in this by means of colorful examples:
Simple Present Tense
Covers daily rituals, immortal facts and whatever is etched in stone, such as train times or bad coffee addictions.
Present Continuous Tense
States what is occurring at this very moment or some time soon. Applied to things under process, temporary or arrangements that are planned in the short term.
Present Perfect Tense
The tense concentrates on what has been made and not when it was made. It is ideal for discussing life experiences, newsworthy events or current outcomes.
Present Perfect Continuous Tense
Displays an activity which began in the past tense in English but is continuing or has just paused.
Present Simple is for general truths, Continuous for current actions, Perfect for completed past actions with present relevance, and Perfect Continuous for ongoing actions that started earlier and still matter now.
Past tenses
Simple Past Tense
Refers to past moments that have ended, giving you a clean-cut view of what happened at that point in time.
Past Continuous Tense
Concentrates on what someone was doing at a given time in the past and notes that some activity was taking place and not accomplished.
Past Perfect Tense
Shows completion of one past event relative to another. It’s useful for explaining cause and effect in the past.
Past Perfect Continuous Tense
Makes emphasis on the duration, which indicates that an action occurred prior to another event in the past. It tends to respond to “how long?” questions of past events.
Past tenses in English grammar enable you to make a statement of what transpired and how things worked out during a certain period of time. The right tense emphasizes the order of events, the length of time, and the situation in an attempt to make any story or description understandable.
Future tenses
Simple Future Tense
For plans, predictions, or quick decisions.
Future Continuous Tense
Meant to discuss current plans, predictions, or hasty judgments. It gives the message of what one intends to do or what could occur in the future.
Future Perfect Tense
States the accomplishment of activities or occurrences by a specified future time. It usually provides the answer to the question of what will be happening by that time.
Future Perfect Continuous Tense
Show the length of time an activity will have continued before a future moment arrives. It focuses on the ongoing nature and persistence of the action.
How to choose the right tense in English?
The optimal tense choice may be treated as a grammatical labyrinth in the majority of cases, but it is only a question of answering one question, and that is when it happens.
In regard to the right tense, it renders your sentence clear and flowing, besides being accurate, just as is the case when relocking your lock with the correct key. Learn English tenses thoroughly, and you’ll start using them without a second thought.
Step 1: Determine time frame
Determine the time the action occurs first:
- Now? Present tense
- Already happened? Past tense
- Will it happen later? Future tense
Step 2: Consider the action’s duration and completion
Now the question: Is it still happening, is it done, or is it something that has been happening repeatedly?
| Action type | Use this tense | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Regular/repeated | Simple | He |
| Happening now | Progressive | He |
| Just finished/affects now | Perfect | He |
| Ongoing up to a point | Perfect Continuous | He |
Step 3: Think about the context
Tenses in the English language will rely on what you would like to stress:
Time order → Past Perfect
Present relevance → Present Perfect
Intended or timed activity → Future Simple
Emphasis on duration → Progressive
Step 4: Remain consistent
Don’t hop between different tenses in English unless there’s a clear reason. Keep the timeline consistent within a sentence or paragraph, especially in storytelling or instructions.
Quick guide to picking the correct tense
- Use present tenses for facts, habits, and general truths.


- Use past tenses for storytelling and completed actions.
- Use future tenses to express predictions, intentions, or scheduled plans.
- Use perfect tenses to connect actions across time or show completion.
- Use continuous tenses to zoom in on something happening over time.
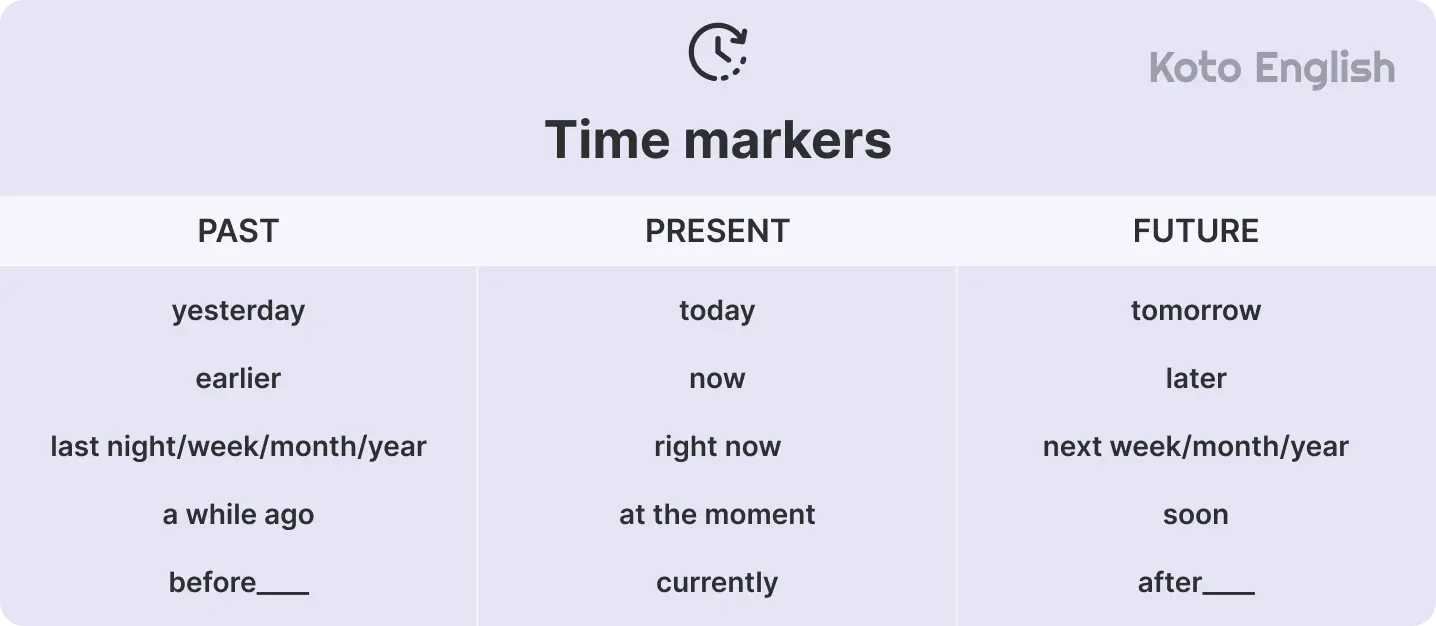
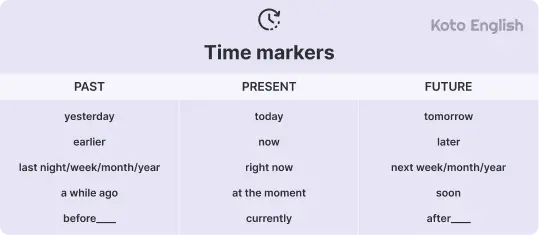
Time markers for tenses
Time indicators are the posts of tenses in the English language. They inform your listener or your reader when something occurred, occurs and will occur.
No matter whether you are speaking about the past, present, or future, with the correct use of the time marker, you will use it to put the action that you are speaking about on the timeline in a natural and clear way.
Present tenses: ongoing, habitual, or current
These tenses in English grammar denote the current events, what is mostly the case or what takes place regularly.
Present Tenses: Ongoing, Habitual, or Current
These tenses denote the current events, what is mostly the case or what takes place regularly.
| Tense | Common time markers | Example sentences |
|---|---|---|
| Present Simple | always, usually, often, rarely, never, every morning/Monday/year |
He always
They rarely
|
| Present Continuous | now, at the moment, currently, today, this week |
I
Right now, she
|
| Present Perfect | already, just, yet, ever, never, recently, since, for |
He
We
|
| Present Perfect Continuous | for, since, all day, lately, recently, the whole week |
They
You
|
Together, these forms let you handle everything from “right now” to “still going” without skipping a beat.
Past Tenses: completed or ongoing in the past
All English tenses in the past are used to indicate some action that has occurred previously at some given point in time, either completed or partly completed.
| Tense | Common time markers | Example sentences |
|---|---|---|
| Past Simple | yesterday, last week/month/year, ago, in 2010, when I was a kid |
She
He
|
| Past Continuous | while, when, at 7 PM yesterday, during, as |
I
They
|
| Past Perfect | before, after, by the time, already, just, until then |
She
They
|
| Past Perfect Continuous | for, since, all day, the whole morning, how long |
He
I
|
Understanding these tenses means you can tell any past story confidently, highlighting what happened, when, and for how long.
Future tenses: schemes, forecasts, or projections
Future grammatical tense is applied in acts which will occur later on, but are anticipated to.
| Tense | Common time markers | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Simple Future | tomorrow, next week/month/year, soon, in 5 minutes, later |
She
She
|
| Future Continuous | this time tomorrow, at 8 PM next Friday, during, while |
Tomorrow around now, they
They
|
| Future Perfect | by then, by the time, before, already |
By next month, she
I
|
| Future Perfect Continuous | for, since, by then, how long |
By the end of the concert, the band
They
|
Future tenses turn your ideas about tomorrow into sharp, vivid stories that anyone can follow.
Typical mistakes in time expressions
Even the most confident learners of English occasionally stumble around the so-called time expressions, namely those small and powerful phrases which put actions into the time table.
Their use, or altogether misplacing them, can make your entire message really grind to a halt or spend some time in really awkward grammar encounters.
- Confusion of Present Perfect with specific Past times
Adding a particular time (such as yesterday or last year) violates the rule.
|
He has bought a new phone yesterday.
|
He bought a new phone yesterday.
|
|
Jack has broken his leg last summer.
|
Jack broke his leg last summer.
|
- Since is used instead of for
Since is used in beginning points, and for is used in duration.
|
Liam has been waiting since three hours.
|
Liam has been waiting for three hours.
|
|
We have been exploring the city since six hours.
|
We have been exploring the city for six hours.
|
- Failing to use ago in the Past tense
The word ago refers to a finished point in time, so it should always be used with the Simple Past, not the Present Perfect.
|
Emma has bought a new guitar two weeks ago.
|
Emma bought a new guitar two weeks ago.
|
|
The team has won the championship in 2020.
|
The team won the championship in 2020.
|
- Switching tenses mid-sentence without logic
Jumping from past to present without a reason leaves your reader confused.
|
She was tired, so she takes a nap.
|
She was tired, so she took a nap.
|
|
Daniel missed breakfast, so he eats a sandwich at work.
|
Daniel missed breakfast, so he ate a sandwich at work.
|
- Using did + past verb
In questions or negatives with did, the main verb stays in base form.
|
Did she forgot her keys again?
|
Did she forget her keys again?
|
|
Did we watched the movie together?
|
Did we watch the movie together?
|
- Misusing and confusing by and until
Use by when something needs to be completed before a certain moment. Use until when something is happening during that time.
|
She waited by the rain stopped.
|
She waited until the rain stopped.
|
|
Maria cried by her friend comforted her.
|
Maria cried until her friend comforted her.
|
- Confusing used to and be used to
Used to = past habit. Be used to = accustomed to something (noun/gerund).
|
She is used to go to bed late.
|
She used to go to bed late during college.
|
|
We are used to watch TV after dinner.
|
We used to watch TV together as kids.
|
Using time phrases correctly adds precision and polish to your English. Learn to spot and fix these errors, and you’ll communicate with ease and style.
Enjoy personalized learning!
Practice time
It’s time to level up your tense game. These exercises mix recognition, grammar logic, and real-life communication to help you master what time expressions really do and answer the big question: what are tenses in English, and how can you use them effortlessly in daily speech?
Tips for mastering usage
Getting fluent in English tenses is not about stuffing your brain with a huge set of rules: it is, first of all, the development of the sense of timing the events and the selection of the most suitable form. This English tenses overview with guidelines will assist you in being punctual (in grammatical terms):
- Think in time frames
What should we ask before selecting a tense:
- What time period is the action taking place in: past, present, or future?
- Is it finished or still happening?
This mental habit imparts a native feeling of the use of tenses.
Telling a childhood experience? Capitalize on the past.
Giving an account of an existing habit? Your friend is Present Simple.
Having some intuition? You are on the way to the future.
- Spot the time markers
The usage of such words as yesterday, already, tomorrow, and always signifies the tense that should be used. Consider them as hints.
Draw a simple timeline on paper. Place your verbs on it — past, present, future. This helps you see when things happen, especially when dealing with perfect and progressive forms.
- Perfect tenses should not be overused
Perfect tenses are convenient, and when used too often, they are unnatural. You can follow them when presenting a relationship between time spans, not all past actions. The things that used to be instead of:
|
I have eaten lunch at noon yesterday.
|
I ate lunch at noon yesterday.
|
- Training with a real-life situation
Sentences in books are okay, but your mind remembers quicker using examples of your own. Talk or write about your personal history, what you intend to do today or tomorrow.
You may try:
- Use the past tense to describe your most recent vacation.
- Discuss your morning routine in the present tense.
- Think about your existence in 2030. Use the Future Continuous to describe it.
- Use the Future Perfect to share a goal you plan to accomplish before the end of this year.

- Purposeful watch and read
Contextual use of tense is abundantly found in movies, articles, published books, and podcasts. Notice the way in which characters move back and forward through time or catapult themselves into the future and what the reason is.
Next time you watch a movie, turn on subtitles and track verb forms.
- Try your hand at mini-stories
Write a tale in three sentences using each tense. Try merging them into a single timeline after that. This strengthens the flow and contrast. For instance:
- Practice with smart tools
Tense grammar checkers, flashcards and interactive apps assist you in detecting patterns and tense mastery in the long run. Look for ones that offer instant feedback and practical examples.
Try Koto English for a comprehensive experience where you are able to study English grammar tenses and grasp them through active use. Indeed, pronunciation, vocabulary, and natural speaking flow are all covered.
Conclusion
The English tenses are the structure that provides every sentence with a definite understanding of time. They enable you to demonstrate when things occur, the duration of action and the relationship between various events. The appropriate use of the tense will transform ordinary sentences into a narrative, guidelines, or observations, which are meaningful and can be easily understood.
Paying attention to context, time markers, nature of the action helps select the right grammar tense in any situation. With consistent practice and Koto English, you can handle past, present, and future events naturally, expressing ideas with accuracy and confidence.
Times in English FAQ
The English language makes use of tenses of verbs to give a clear and appropriate usage of time. There are 12 principal types of tenses, which are categoriяed by time and aspect.
- Three periods: Present, Past, Future
- Four aspects: simple, continuous (progressive), perfect, perfect continuous
- All four aspects are contained in each time frame, leading to the formation of 12 combinations
It is a structure where you can not only reveal the occurrences of the time but also you can reveal how long, how frequent, or what has been accomplished. Learning these forms makes your communication clearer and more complex.
The Present Simple is the workhorse tense of the English language. It is used day in day out by people to discuss habits, facts and truth in general. It is simple and can multitask — ideal to talk when nothing much happens.
Many students find the most difficulties with the Perfect tense (as well as the Perfect Continuous tense) which denote the completion, the duration and the relation to another time point. There are also the deceptive Future Simple forms, which refer to the things that will be done or are being done by a future date.
To begin with, locate the time period: past, present, or future. Next, deliberate on whether the action is completed, in process or repetitive. The context markers of times in English, such as time (e.g, yesterday, now, soon), are useful in determining the proper tense. With time, intuition will be developed through reading and listening a lot.
All tenses in English need not be a boot camp in grammar. It is just a matter of making it a daily activity, but doing it without making it a duty.
- Read, watch, and listen to English stories, shows, and podcasts.
- Keep a daily journal and write about your day using different English grammar tenses.
- Endlessly talk to yourself aloud when you are accomplishing little things in your life: (I am preparing coffee, I will clean the kitchen).
- Make use of applications or flashcards that highlight context-based time cues.
- Take part in online discussions or language partner interactions where you receive a live evaluation.
You will no longer be in doubt but you will use the right tenses in grammar without pondering much.
Verb time expressions give your writing clarity and structure, showing when actions happen and how they relate to each other. Proper use of tenses will allow the reader to go through lines, comprehend the sequence, and interpret happenings in a proper manner. It is impossible to read even the most interesting story or teaching without it and get lost or confused.




