What is the Present Perfect tense?
Present Perfect tense meaning can be understood as a way to link past actions to the present moment. It’s often used for life experiences, completed tasks with present results, and changes over time. Its ability to link past and present makes it ideal for real-world communication — from resumes to casual conversations.
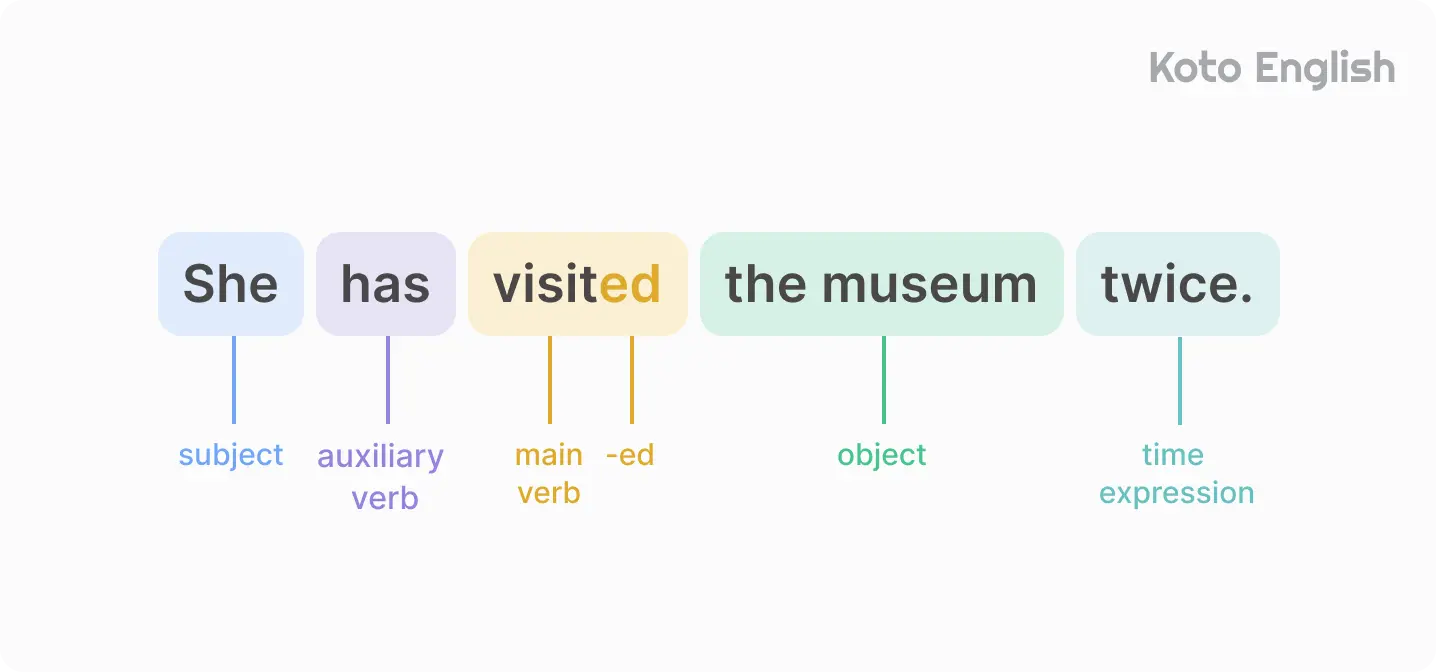
We’ll explore the finer points to help you master this tense.
Present Perfect tense examples:
Level up your English with Koto!
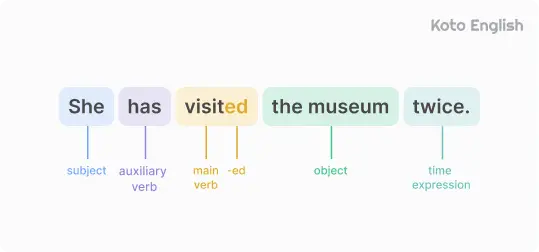
Present Perfect tense formula
In the Present Perfect structure, we use have/has plus the past participle of the main verb. For regular verbs, just add -ed to the root form, but for irregular verbs, the past participle forms are irregular and must be memorized.


Take a look at these Present Perfect sentences to understand how they’re applied.
| Subject | Examples |
|---|---|
| I |
I
|
| You (singular) |
You
|
| He |
He
|
| She |
She
|
| It |
It
|
| You (plural) |
You
|
| We |
We
|
| They |
They
|
Remember, the Present Perfect tense is not used with specific time expressions like yesterday or last year — it focuses on the connection between the past and the present, not the exact timing of an action.
When to use Present Perfect?
The Present Perfect expresses actions that occurred in the past, but whose outcomes influence or relate to the present moment. It’s ideal for describing actions that started in the past and continue up until now, or actions with a present consequence.
Present Perfect examples:
| Usage | Examples |
|---|---|
| Actions completed by an unspecified time, with impact now |
I
|
| Simultaneous events with ongoing relevance |
He
|
| Actions completed before now, with a visible result |
They
|
| Describing personal growth or life experiences |
We
|
Present Perfect tense markers:
| Time indicators | Examples |
|---|---|
| already |
She
|
| ever |
Have you
|
| before |
We
|
| yet |
I
|
| just |
They
|
| lately/recently |
He
|
| For + time period |
They
|
| since |
We
|
Use it to build suspense: It’s great for storytelling — “Something strange has happened…”
How to use Present Perfect
So far, we’ve explored the Present Perfect definition and gone through plenty of examples of affirmative sentences. Now, it’s time to flip the script and dive into how to form negatives and questions — each with its own twist.
The negative form of the Present Perfect
To express something that hasn’t happened, insert not after the auxiliary verb. You’ll get have not or the contraction haven’t, and has not or hasn’t for third-person singular. Simple, yet powerful!


Examples of the Present Perfect tense in negation:
Present Perfect example of negative patterns:
| Subject | Full form | Short form |
|---|---|---|
| I |
I
|
I
|
| You (singular) |
You
|
You
|
| He/She/It |
She
|
She
|
| We |
We
|
We
|
| They |
They
|
They
|
| You (plural) |
You
|
You
|
Enjoy personalized learning!
Present Perfect Questions
Forming questions in the Present Perfect is simple once you get the hang of it. Just switch the subject and the auxiliary verb have or has to create a question.
Yes/No Questions

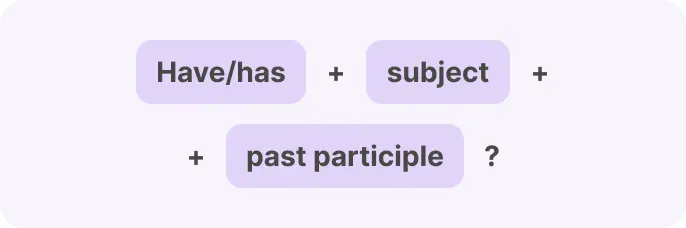
Present Perfect tense example in Yes/No questions:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
|
|
Yes, they
|
|
|
No, we
|
|
|
Yes, he
|
Wh-questions

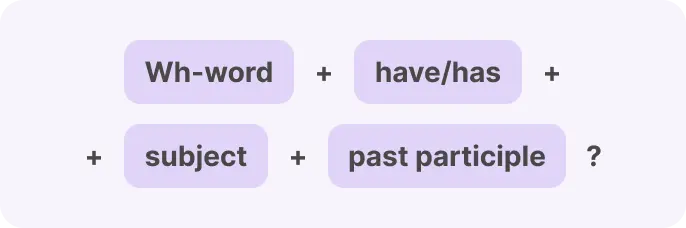
Example of Present Perfect tense with Wh-word questions:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
|
Why
|
I
|
|
Who
|
Sarah, John, and Emma
|
|
How
|
I
|
For emphasis, use yet in questions to ask if something has occurred up to the present.
Common mistakes with the Present Perfect in English
Understanding when to use the Present Perfect tense can be challenging, as it bridges past events with the present. Here are some typical mistakes learners tend to make while using this tense.
Using specific time expressions with the present perfect
The Present Perfect is used for actions that are not tied to a specific time reference, but learners often mistakenly use specific time expressions.
|
We have watched that movie last night.
|
We watched that movie last night.
|
|
She has met him two weeks ago.
|
She met him two weeks ago.
|
Mixing the Present Perfect with time expressions like for and since incorrectly
Using for and since with the present perfect can be tricky, especially when learners try to mix them with ago.
|
I have been friends with him since five years ago.
|
I have been friends with him for five years.
|
|
They have lived here for ten years ago.
|
They have lived here for ten years.
|
Using the Present Perfect for actions that are not relevant to the present
The use of the Present Perfect tense isn’t just about the past — it’s about the past’s relevance to the present. Learners sometimes miss this connection, forgetting that the Present Perfect shows how past actions or experiences continue to affect the present moment.
|
He has lost his keys at the party yesterday.
|
He lost his keys at the party yesterday.
|
|
You has eaten pizza last night.
|
You ate pizza last night.
|
Summary
The Present Perfect is a tense that bridges the past and the present, allowing you to describe events that affect your current situation. So, what is the Present Perfect? It’s a tense that highlights the connection between past actions and their ongoing relevance or effect.
With its ability to show this link, you’ll be able to express your experiences and accomplishments like a pro. Keep honing your skills, learn Present Perfect tense rules, and soon it’ll become second nature!
Present Perfect tense FAQ
Common time expressions with the Present Perfect include since, for, ever, never, lately, and yet. These are used to link past actions or events to the present.
The Present Perfect connects past actions or experiences with the present moment, while the Simple Past refers to actions that happened at a specific time in the past, with no direct link to the present.
| Present Perfect | Simple Past |
|---|---|
|
I
|
I
|
The Present Perfect is helpful when talking about experiences, changes, and actions that impact the present. It’s commonly used to reflect on past accomplishments or significant events.
This tense can trip people up, especially when it’s used with the wrong time expressions or mistaken for the simple past. Here are a few classic blunders (and how to dodge them):
- Yesterday is a specific time — use Past Simple, not Present Perfect.
|
I have met him yesterday.
|
I met him yesterday.
|
- Irregular verbs like eat take the past participle form — eaten.
|
Have you ever ate sushi?
|
Have you ever eaten sushi?
|
- Has is for he, she, it — have for you, we, they.
|
Has you ever been to Brazil?
|
Have you ever been to Brazil?
|






