What is the Past Simple tense?
The Past Simple rules emphasize that this tense is used specifically for actions that are seen as completed, usually at a definite point in the past. It doesn’t require any connection to the present, making it distinct from other tenses like the Present Perfect.
This tense is simple yet powerful, as it allows speakers to clearly mark when an event occurred without complicating the timeline.
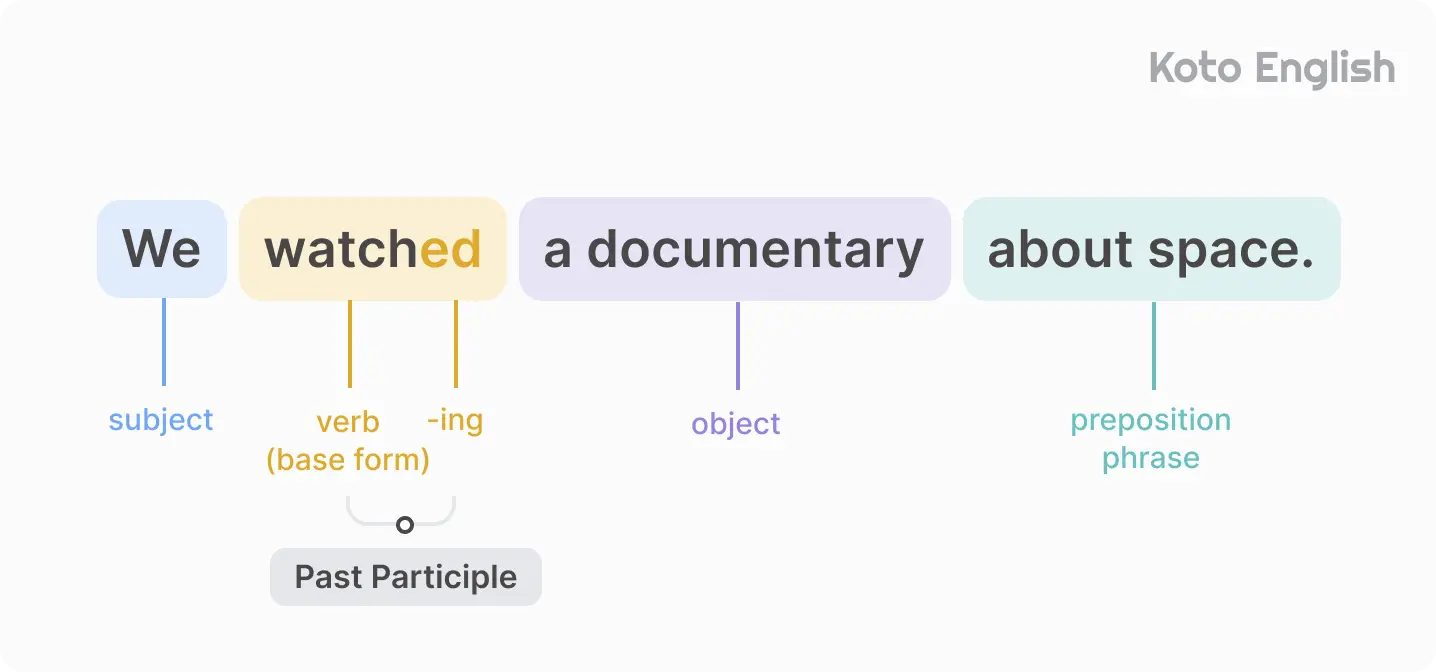
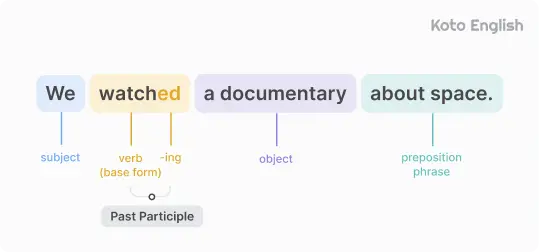
Past Simple examples:
Level up your English with Koto!
Past Simple structure
To form Simple tense add -ed to regular verbs, while irregular verbs have unique past forms.
The Past Simple formula looks like this:




Below is a table showcasing different Past Simple tense examples of structures with various subjects:
| Regular verb (-ed form) | Irregular verb (unique past form) |
|---|---|
|
I |
Kids |
|
The student |
You |
|
Sarah |
He |
|
We |
Friends |
|
They |
Michel |
|
My wife |
Henry |
When to use Past Simple?
The Past Simple is ideal for highlighting finished actions, repeated past behaviors, or factual events, focusing solely on the past without any present connection.
Past Simple example of usage:
| Usage | Examples |
|---|---|
| Completed action in the past |
She
|
| Past habit or routine |
Brian
|
| Specific past event |
We
|
| Historical fact |
The Wright brothers
|
| Series of past actions |
May
|
Tense markers of Past Simple:
| Time indicators | Examples |
|---|---|
| Yesterday |
The cat
|
| Last week/month/year |
Luca
|
| Two days ago |
The old man
|
| Years in the past |
The library
|
| A few days ago |
A family
|
| When someone was a child |
My father
|
| Earlier today |
The baker
|
| Last night/morning/evening |
The owl
|
| In the past |
The knight
|
| Once |
Tommy
|
When using this tense, remember that it does not concern the duration of the action or any link to the present, as it simply describes actions that happened and ended in the past.
Here are some frequently used regular verbs in the Simple Past tense:
| Base Form | Past Simple | Base Form | Past Simple |
|---|---|---|---|
|
play
|
play
|
work
|
work
|
|
talk
|
talk
|
watch
|
watch
|
|
clean
|
clean
|
help
|
help
|
|
start
|
start
|
visit
|
visit
|
|
walk
|
walk
|
call
|
call
|
|
like
|
lik
|
jump
|
jump
|
|
paint
|
paint
|
travel
|
travel
|
|
enjoy
|
enjoy
|
||
And, of course, we recommend exploring these commonly used irregular verbs in the Simple Past:
| Base Form | Past Simple | Base Form | Past Simple |
|---|---|---|---|
|
go
|
went
|
eat
|
ate
|
|
have
|
had
|
be
|
was/were
|
|
do
|
did
|
see
|
saw
|
|
make
|
made
|
get
|
got
|
|
take
|
took
|
come
|
came
|
|
say
|
said
|
give
|
gave
|
|
know
|
knew
|
run
|
ran
|
|
find
|
found
|
speak
|
spoke
|
|
buy
|
bought
|
meet
|
met
|
|
sleep
|
slept
|
write
|
wrote
|
Unlike regular verbs, which form the past tense by simply adding -ed to the base form (e.g., “work” becomes “worked“), irregular verbs do not follow a consistent pattern. Each irregular verb has its unique past form.
How to use the Past Simple tense?
To build positive Past Simple sentences, you need to use the past form of the verb. For regular verbs, this typically means adding -ed to the base form, while for irregular verbs, the Past Simple form varies and needs to be memorized.
We’ve already covered how regular and irregular verbs are used to form these positive statements, so now it is time to talk about other types of sentences.
Negative form
For negative sentences in the Past Simple, we use did not (or its contraction didn’t) followed by the base form of the verb. The verb does not change to the past form after didn’t because did already indicates the past tense.


Look at some examples of Past Simple negative sentences:
| Full form | Short form |
|---|---|
|
My grandparents
|
My grandparents
|
|
The chef
|
The chef
|
|
The scientist
|
The scientist
|
|
The birds
|
The birds
|
|
The teacher
|
The teacher
|
|
The actor
|
The actor
|
Enjoy personalized learning!
Past Simple questions
In the Past Simple, questions are made by inverting the subject and the auxiliary did.
Yes/No questions


Let’s see how it works in conversations:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
|
|
No, he
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Wh-questions


Let’s see how it works in conversations:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
|
Where
|
She
|
|
Why
|
He
|
|
When
|
They
|
Common mistakes with the Simple Past in English
Even though the Past Simple is straightforward, learners often make errors when forming and using it. Here are some of the most frequent mistakes and how to avoid them.
Using the base form instead of the past form
Some learners forget to change the verb to its past form when talking about completed actions.
|
She go to the store yesterday.
|
She went to the store yesterday.
|
|
They take a taxi to the airport.
|
They took a taxi to the airport.
|
Regular verbs take -ed in the past, while irregular verbs have unique past forms that must be memorized.
Overusing ‘did’ in positive sentences
Did is only used in negative sentences and questions, not in affirmative statements.
|
He did went to the party last night.
|
He went to the party last night.
|
|
They did bought a new house.
|
They bought a new house.
|
In positive sentences, just use the past form of the verb without did.
Forgetting ‘did’ in questions and negatives
In Past Simple, negatives and questions require did, and the main verb stays in its base form.
|
She not like the movie.
|
She did not like the movie.
|
|
Where you go last summer?
|
Where did you go last summer?
|
Always use did in negative sentences and questions, while keeping the main verb in its base form.
Confusing Past Simple and Present Perfect
The Past Simple goes with specific time markers, while the Present Perfect is used for unspecified time or experiences.
|
I have seen that movie yesterday.
|
I saw that movie yesterday.
|
|
He has met her at the party last weekand?
|
He met her at the party last weekend.
|
As you have already read here, Past Simple is used with words like yesterday, last year, two days ago, while the Present Perfect is for experiences without a specific time.
I
Summary
The Past Simple is the go-to tense for talking about finished actions and past events. It allows you to describe what happened at a specific time and makes storytelling more precise. Learning the Past Simple definition, its structure, and common mistakes will help you use it naturally in conversations and writing.
Past Simple tense FAQ
When do we use did in the Past Simple tense?
| Question | Negative |
|---|---|
|
|
I
|
The Past Simple refers to a completed action at a specific point in the past, while the Present Perfect connects past actions to the present or focuses on their relevance now.
| Past Simple | Present Perfect |
|---|---|
|
He
|
He
|
The Past Simple of irregular verbs does not follow the regular -ed pattern and must be memorized. Each verb has a unique past form.
come → came
Many slip-ups happen when people juggle irregular verbs or forget the trusty auxiliary did in negatives and questions. Let’s shine a light on the sneaky ones:
- Rule reminder: After didn’t, use the base form of the verb.
|
I didn’t saw him at the park.
|
I didn’t see him at the park.
|
- The auxiliary did already carries the past tense — don’t double up.
|
Did she called you back?
|
Did she call you back?
|
- Negatives in past simple need didn’t + base verb — no shortcuts!
|
He not remembered my birthday.
|
He didn’t remember my birthday.
|








