What is the Present Simple?
The Present Simple is the verb tense used to speak about actions that repeat, sometimes, never, or always. It is also for habitual things we do, like when we drink tea every morning or read a book before sleep.
The tense is also called Simple Present or Present Indefinite. It is easy to build sentences in this tense, but there are a few nuances you need to know to understand it fully.
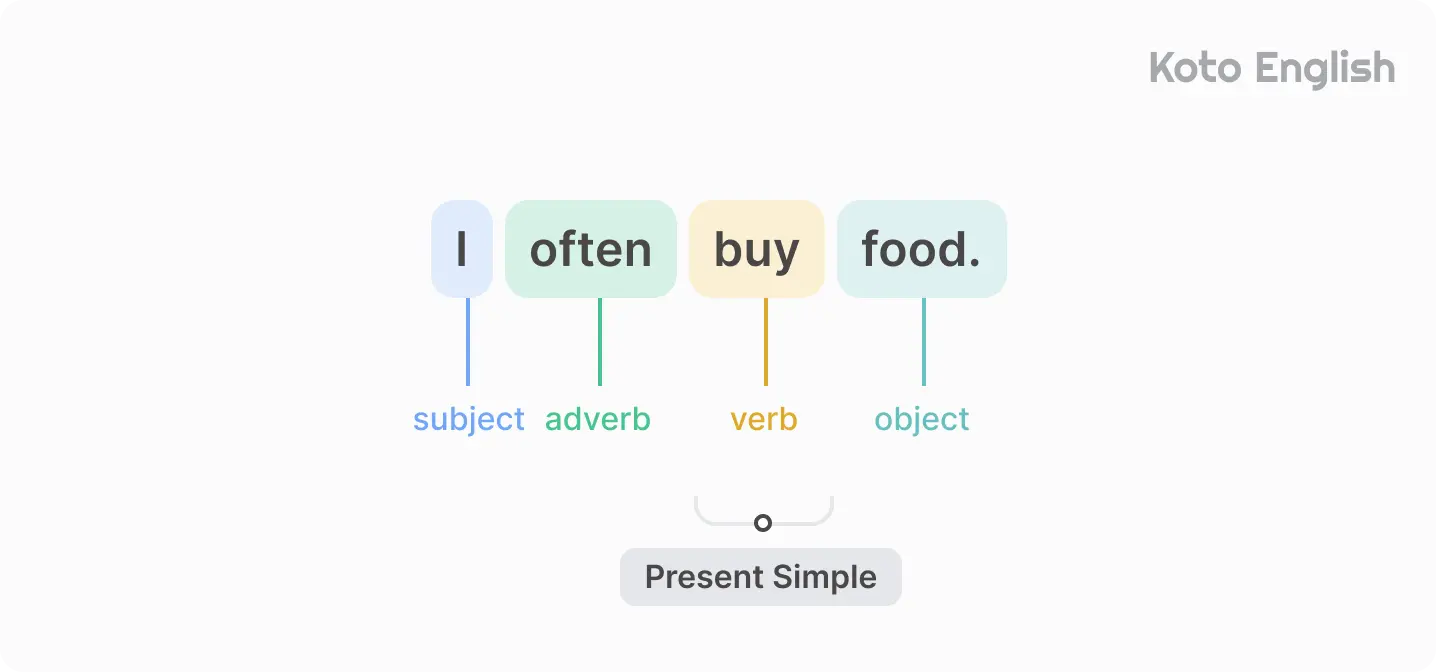
Examples of Simple Present:
Level up your English with Koto!
Present Simple structure
The structure of the Present Simple is easy and only touches the verb. To form a sentence, you need to take the base form of the verb (to run, to meet, to walk, to cook).
Then you add -s or -es ending to the verb if it is a third-person singular (he, she, it). The other subjects (I, you, we, they) go with a bare infinitive — the root form without the particle to.


Look at how the verb changes based on the person:
| Subject | Structure of Present Simple |
|---|---|
| I |
I
|
| You |
You
|
| He |
He
|
| She |
She
|
| It |
It
|
| We |
We
|
| They |
They
|
| You (plural) |
We
|
To memorize the grammar quickly, practice with your daily routine. Write what you do every day by the hour.
When do we use the Present Simple?
There are many cases of using the Present Simple. You can even write a short article on any topic using only this tense — it illustrates its usefulness.
Take a look at the cases and Present Simple tense examples below:
| Usage | Examples |
|---|---|
| Repetitive, habitual actions |
I
|
| States and conditions |
I
|
| General truths or facts |
The USA
|
| Scheduled events in the future |
The plane
|
| Instructions |
|
| Pointing direction |
|
| Phrases with adverbs of frequency |
I always
|
Tense markers
In Present Simple, these words help you to show the repetitiveness of some action, your schedule, daily routine, habits, and so on. Check the sentences to see how it works:
| Time indicators | Present Simple examples |
|---|---|
| Always, usually, sometimes, rarely, never. |
I
|
| Every day/week/month. |
He visits his grandparents
|
| Once a year, twice a week, three times a month. |
You
|
| On Sundays, on Mondays, on Tuesdays. |
We
|
| In the morning, in the afternoon, in the evening, |
They
|
| At 7 a.m., at 5 p.m. |
You
|
Long phrases like once a week, every month, or in the morning typically go to the end of the sentence in the Present Simple sentences. Adverbs of frequency (always, usually, sometimes) are placed after the subject (I, You, They) and before the verb (go, visit, spend).
How to use the Simple Present tense?
We discussed the Present Simple definition and the cases of its usage. Now, let’s explore other nuances that will help you to learn English effectively.
Affirmative sentences
If you want to say that something is a fact or it happens regularly, you use affirmative, or positive, sentences. Here, you need the formula you learned before:


Here are some sentences for more understanding:
| Subject | Example |
|---|---|
| I |
I
|
| You (singular) |
You
|
| He/She/It |
She
|
| We |
We
|
| They |
They
|
| You (plural) |
You
|
Negative sentences
Creating a negative sentence in the Simple Present tense requires us to add a special auxiliary verb:


Examples:
In negative sentences, we can use both long forms and constructions. The short Present Simple form is constructed by joining the words do not and does not:
Let’s refer to some examples:
| Subject | Full form | Short form |
|---|---|---|
| I |
I
|
I
|
| You (singular) |
You
|
You
|
| He/She/It |
He
|
He
|
| We |
We
|
We
|
| They |
They
|
They
|
| You (plural) |
You
|
You
|
Questions
To create questions in Present Simple, we take do and does and put them at the beginning. The subject follows the auxiliary word, and the main verb comes after the noun.
Yes/no questions




Take a look at examples of such sentences:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
|
|
I
|
|
|
|
|
|
They
|
WH-question


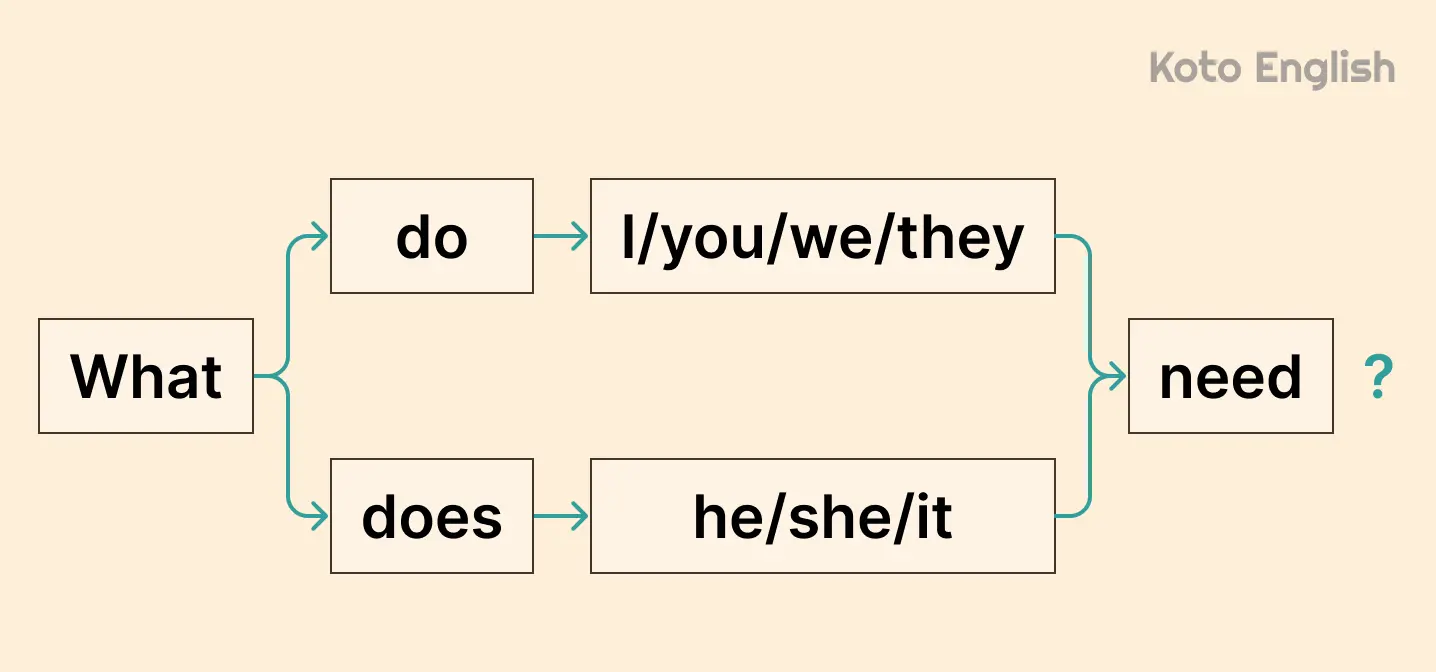
Let’s look at examples:
| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
|
|
I
|
|
|
He
|
|
|
They
|
We change the form of the verb when the sentence is positive, but when it is negative, or a question, do and does indicate the tense, so we don’t add any endings.
That’s why: Does he work here?
But not: Does he works here?
The verb to be
We don’t use the auxiliary words when there are no verbs in the sentence. That’s why when we want to say that we are not happy or ask if another person is tired, we need to know the rules of using the verb to be in the Present Simple.
It has three forms, which we use based on our subject.
Only by using this grammar structure can you tell a lot about yourself.
Present Simple uses with to be:
| Positive | Negative | Questions |
|---|---|---|
|
I
|
I
|
|
|
He
|
He
|
|
|
She
|
She
|
|
|
It
|
It
|
|
|
You
|
You
|
|
|
We
|
We
|
|
|
They
|
They
|
|
Spelling rules for Simple Present
To build correct sentences, you need to learn how the verbs change in this tense. We prepared easy and detailed explanations you can find below.
When to add -s
We said before that the ending can be -s or –es, and now we’ll explain practical tips in the affirmative sentences you can use to state some facts or situations.
| Base form + -s ending | Example |
|---|---|
| walk → walk |
Your sister
|
| eat → eat |
His cousin
|
| wait → wait |
Jeremy
|
| work → work |
Samantha
|
When to add -es
After the verbs that end in these letters: –ch, –ss, –sh, –x, –o we need to add –es:
| Base form + -es ending | Example |
|---|---|
| catch → catch |
My friend
|
| pass → pass |
My cousin always
|
| wash → wash |
This machine
|
| fix → fix |
That master
|
The spelling for words ending in –y requires removing the last letter and instead putting –ies:
| Base form + -ies ending | Example |
|---|---|
| study → stud |
AI
|
| cry → cr |
My daughter sometimes
|
| try → tr |
She
|
| reply → repl |
He always
|
| Base form + -s ending (after y) | Example |
|---|---|
| stay → stay |
She
|
| play → play |
It
|
| enjoy → enjoy |
He
|
| say → say |
She always
|
There are also some irregular cases. For instance, the verb to have changes into has.
Irregular forms
There are some verbs that you need to memorize in order to use them correctly in Present Simple tense.
| Verb | Example |
|---|---|
| be → am/are |
I
You
|
| have → has (he/she/it) |
She
|
| do → does (he/she/it) |
He
|
Common verbs in the Present Simple
It means the most popular verbs that all speakers use in daily communication, through chats, emails, office meetings, at school, and more. In the table below, you will find some examples according to the categories.
| Type | Verbs | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Action | make, go, do, play, cook |
Father
|
| Stative | know, have, like, want |
I
|
| Sense | see, smell, hear, feel |
You need to
|
With these verbs, you can tell about your daily routine, your wishes, some facts, preferences, and even more.
Common pitfalls to watch out for
The Present Simple rules are not complicated. But it is easy to make many mistakes when you use it. We collected the most repetitive errors for you to know what to focus on:
Choosing to be form instead of do and does
Remember, the main difference between these two cases is that we choose do and does when there is a verb in a sentence, an action, or a state (to run, to feel, know, to study the Present Simple), and we use am, is, are when a subject is followed by adjectives (happy, smart, nervous, hungry, thirsty):
|
I am not agree with you.
|
I don’t agree with you.
|
|
He is play the guitar.
|
He plays the guitar.
|
Forgetting about auxiliary verbs
Another wrong way of speaking and writing is forgetting about a tense word. It is very important not to ignore it because it is only one indicator of the time we have in a sentence, especially in simple tenses:
|
They not know.
|
They don’t know.
|
|
He not go dancing.
|
He doesn’t go dancing.
|
Misusing auxiliary verbs by a person
Present Simple grammar entirely depends on the person. We always use do or don’t if it is first person singular or second plural. When it is third person singular, we need to spell does or doesn’t.
|
We doesn’t live here.
|
We don’t live here.
|
|
Do she want to buy food?
|
Does she want to buy food?
|
Subjects are more than just he, she, it, or you, we, they. My brother, the sofa, our apartments, my doctor’s wife are also subjects, and it would be good to practice it separately.
Helpful learning tips
The structure of the Present Simple is basic for the more complex English tenses you will learn in the future. It is also important for common communication with people, so you need to master it. Here, you will find some tips from advanced learners that actually work.
Tip 1. Practice daily
The first advice is to exercise every day, even for 5 minutes. You can use quick activities from KotoEnglish that take a little of your time, write down your habits or personal information, like where you live, study, work, or else.
Tip 2. Memorize time expressions
You already saw tense markers that will help you to master this grammar. Remembering them, you will also prepare for tests and will recognize them in daily communication.
Tip 3. Reflect on what you learned
Use flashcards, notes, or recall paper to repeat the grammar, so you will remember it for life. Once in a few days, repeat words, tense structure, time markers, and more.
Tip 4. Integrate Present Simple in your day
This practice is also good for being in the moment. Let’s say you are walking in the park, and form your sentences, like, “The woman walks with a dog,” “The child plays with a car toy.”
Summary
What is the Present Simple tense again? It is a very often-used tense that is used to describe your habits, preferences, states, emotions, and needs. To remember it, we recommend working on all the forms — positive, negative, and questions. Present Simple is your first key to fluent speaking.
FAQ about the Present Simple tense
Yes, you use is, am, are with different subjects. Let’s check some examples:
Yes, you change them for the third person singular he/she/it. In the material above, you can read about adding s-/-es to the ending of these verbs.
Typically, you will use these tense markers in Simple Present:
- always
- usually
- often
- every day
- once a month
- all the time
- in the morning
- generally, etc.
You use the Present Simple to discuss what you do from time to time, once a day, three times a week, or to describe general truths.
If you want to discuss something happening right now, at the moment, you need to use Present Continuous:
Present Simple is a basic tense form that we use to talk about daily activities we repeat, habits, facts, observations, schedules, likes and dislikes, and more. To form this tense, you need to use the formula: subject + verb base form + object.






