What is the Present Continuous tense?
The Present Continuous tense is widely used in English to describe actions happening right now or in the near future. While it may seem more complex than simpler tenses, understanding its structure will help you communicate more naturally.
Let’s explore its usage step by step to make it easy and intuitive.
Present Continuous examples:
Level up your English with Koto!
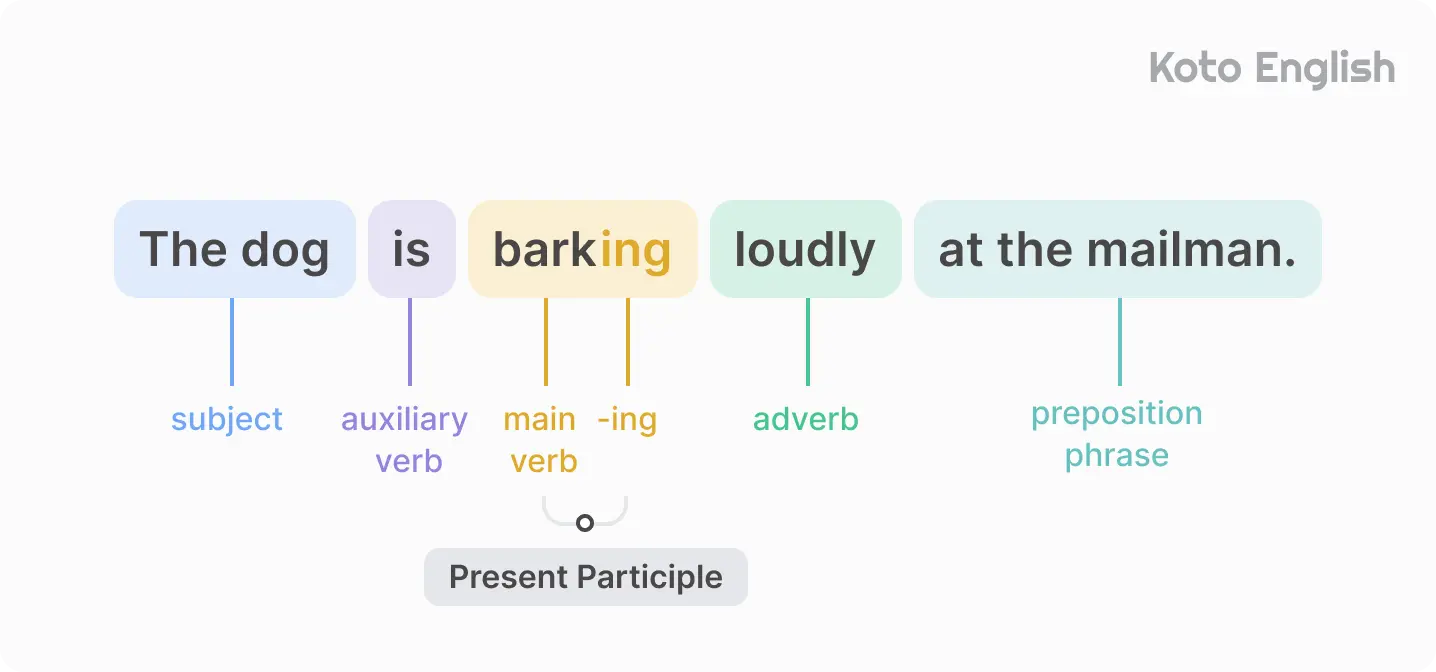
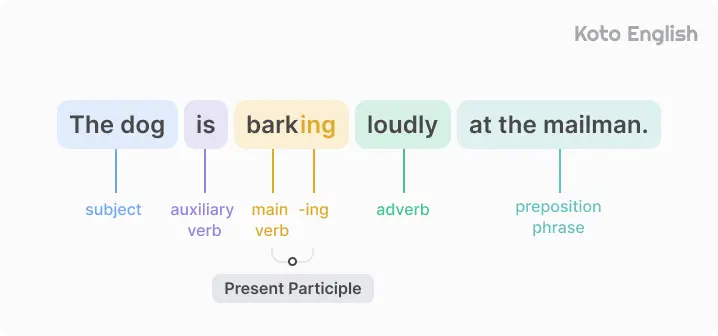
Present Continuous tense formula
Sentences in the tense are formed using am , is , or are (based on subject) + the verb in its -ing form (present participle). This Present Continuous structure helps express actions happening now or planned for the near future.


See how the sentences differ with and without contractions:
| Subject | Full form | Short form |
|---|---|---|
| I | I |
I |
| You | You |
You |
| He/she/it | She |
She |
| We | We |
We |
| They | They |
They |
| You (plural) | You |
You |
When do we use the Present Simple?
The Present Continuous describes what is happening now, temporary situations, or future events planned. It highlights movement and change, unlike the Present Simple, which focuses on routines and facts.
Present Continuous examples of usage:
| Usage | Examples |
|---|---|
| Action in the moment | Watch out! The train |
| Temporary situations | She |
| Future event | We |
| New trend or development | Oversized blazers |
| Processes of change over time | Smartphones |
Tense markers for Present Continuous:
| Time indicators | Examples |
|---|---|
| now, right now | Emma |
| at the moment/present | Grandpa |
| this morning/afternoon/evening/night | Jake |
| this week/month/year | Mia |
| soon | We |
| currently | The zoo |
The Present Continuous tense is ideal for situations where something is in progress or temporarily changing. It emphasizes actions unfolding in real-time or shortly ahead.
How to use the Present Continuous tense?
The verb form follows a clear structure but has a few Present Continuous tense rules to keep in mind. Verbs change by adding -ing, with some spelling adjustments.
We’ll go over everything clearly and simply.
Present Continuous: -ing form spelling
Adding -ing to the base verb is how we create the -ing form for most verbs.
| Base verb → -ing form | Example |
|---|---|
| walk → walk |
She |
| read → read |
He |
| play → play |
They |
| cook → cook |
Mom |
The spelling Present Continuous rules for verbs ending in -e states that the -e must be eliminated before adding -ing to ensure proper verb formation:
| Base verb → -ing form | Example |
|---|---|
| make → mak |
She |
| write → writ |
He |
| drive → driv |
They |
| smile → smil |
The baby |
Before forming the present participle of verbs that end in -ie, replace -ie with -y, then add -ing:
| Base verb → -ing form | Example |
|---|---|
| die → dy |
The plant |
| lie → ly |
He |
| tie → ty |
She |
Enjoy personalized learning!
If a verb concludes with a single consonant preceded by a short vowel, double the consonant before adding -ing to maintain the word’s rhythm:
| Base verb → -ing form | Example |
|---|---|
| run → ru |
She |
| sit → si |
He |
| swim → swi |
They |
| cut → cu |
I |
| plan → pla |
We |
| Base verb → -ing form | Rule |
|---|---|
| rain → rai |
The final consonant isn’t doubled because ai is a long vowel. |
| clean → clea |
The final consonant isn’t doubled because ea is long. |
In British English when a verb ends in a vowel followed by the letter -l, we double the -l before adding -ing:
| Base verb → -ing form | Example |
|---|---|
| cancel → cance |
She |
| travel → trave |
They |
| tell → te |
He |
fail → failing
Verbs ending in -il do not double the -l.
In American English only some of the verbs double -l before adding -ing:
| Base verb → -ing form | Example |
|---|---|
| patrol → patro |
They |
| control → contro |
She |
| compel → compe |
The movie |
Negation of the Present Continuous
For negative sentences in the Present Continuous, not goes right after the auxiliary to be and before the -ing form of the main verb.
Present Continuous formula for negative sentences:


Examples:
The Present Continuous can get a little more relaxed with contractions. For every subject, except I, you have a couple of options: either contract the subject with the verb to be, or join to be with not to create a negative sentence.
Examples of Present Continuous tense in negative form:
| Subject | Full form | Short form |
|---|---|---|
| I |
I
|
I
|
| You |
You
|
You
You
|
| He/she/it |
She
|
She
She
|
| We |
We
|
We
We
|
| They |
They
|
They
They
|
| You (plural) |
You
|
You
You
|
Questions in the Present Continuous
To form questions in the Present Continuous, you switch the position of the subject and the to be verb.
Yes/No Questions


| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
|
|
No, it
|
|
|
No, we
|
|
|
Yes, I
|
Wh-questions


| Question | Answer |
|---|---|
|
|
He
|
|
Where
|
We
|
|
Why
|
I
|
Common mistakes with Present Continuous in English
While the Present Continuous helps us describe actions in progress, it’s easy to slip up. Here’s a guide to avoid common errors and improve your usage of this tense.
Using the Present Continuous with non-action verbs
Some verbs, like know, like, belong, and believe, are not usually used in the Present Continuous because they describe states, not actions.
|
I’m knowing her since last year.
|
I have known her since last year.
|
|
He’s liking that movie.
|
He likes that movie.
|
Stick with the Present Simple for stative verbs (verbs that describe states, not actions) like believe, know, want, etc.
| Non-continuous verbs | ||
|---|---|---|
| Mental states |
think
understand
believe
doubt
|
know
prefer
remember
want
|
| Emotional states |
like
hate
|
love
|
| Senses |
see
hear
smell
taste
|
feel
seem
sound
|
| Possession |
have
possess
|
own
|
| Communication |
agree
disagree
|
mean
promise
|
| Other states |
be
need
owe
|
cost
depend
matter
|
Confusing Present Continuous and Present Simple
The Present Continuous is for actions happening now or in the near future. The Present Simple is for habits or general truths. Don’t mix them up!
|
I’m going to the gym every day.
|
I go to the gym every day.
|
|
She’s always reads books in the evening.
|
She always reads books in the evening.
|
Use Present Continuous for things happening right now, and Simple Present for regular actions or facts.
Forgetting the auxiliary verb in questions
Questions in the Present Continuous require the auxiliary verb to come before the subject.
|
You are watching the game?
|
Are you watching the game?
|
|
Is she goes to school?
|
Is she going to school?
|
Remember, as we mentioned before, in Present Continuous questions, flip the subject and the auxiliary verb: Are/Is + Subject + verb-ing?
Overusing Present Continuous for future plans
Don’t use the Present Continuous for future plans unless they are fixed or scheduled events (e.g., meetings, flights).
|
I’m going to a concert next week.
|
I will go to a concert next week.
|
|
They’re traveling to Spain next summer.
|
They will travel to Spain next summer.
|
Use the Present Continuous only for near-future events that are planned or arranged. Use will or going to for other future predictions or plans.
Summary
So what is the Present Continuous? To wrap it up, this tense is essential for expressing ongoing actions and scheduled events, helping you speak more fluidly in the present moment. With practice, avoiding common mistakes will make it even easier to use.
Present Continuous tense FAQ
We use the Present Continuous to talk about actions taking place right now, temporary conditions, or events you have planned for the near future.
The Present Continuous is for actions in progress or planned for the near future, while the Present Simple is for regular, habitual actions or general truths.
| Present Continuous | Present Simple |
|---|---|
| I |
I |
Verbs that describe states, such as know, like, and believe, are not usually used in the Present Continuous because they refer to conditions or situations, not actions.
|
He is believing in magic.
|
He believes in magic.
|
Except for above mentioned common mistakes (using the Present Continuous with stative verbs, confusing it with the Present Simple, or forgetting the auxiliary verb in questions), here are some more examples of incorrect usage of this tense:
- Using Present Continuous for states of possession:
|
I am owning a car.
|
I own a car.
|
- Using the Present Continuous for general truths:
|
The sun is rising in the east.
|
The sun rises in the east.
|
- Forgetting to use the base form of the verb after the auxiliary verb to be in questions:
|
Is she going to school every day?
|
Does she go to school every day?
|





